FRENECTOMY
What is a Frenectomy and When is it Necessary?
What is a Frenectomy and When is it Necessary?
A frenectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the extraction of one or both frena found in the mouth. Frena are connective tissue membranes that attach one area within the mouth to another. The main frena in the mouth include the following:
- Lingual frenum – A vertical band of slender tissue that connects the tongue to the bottom of the mouth.
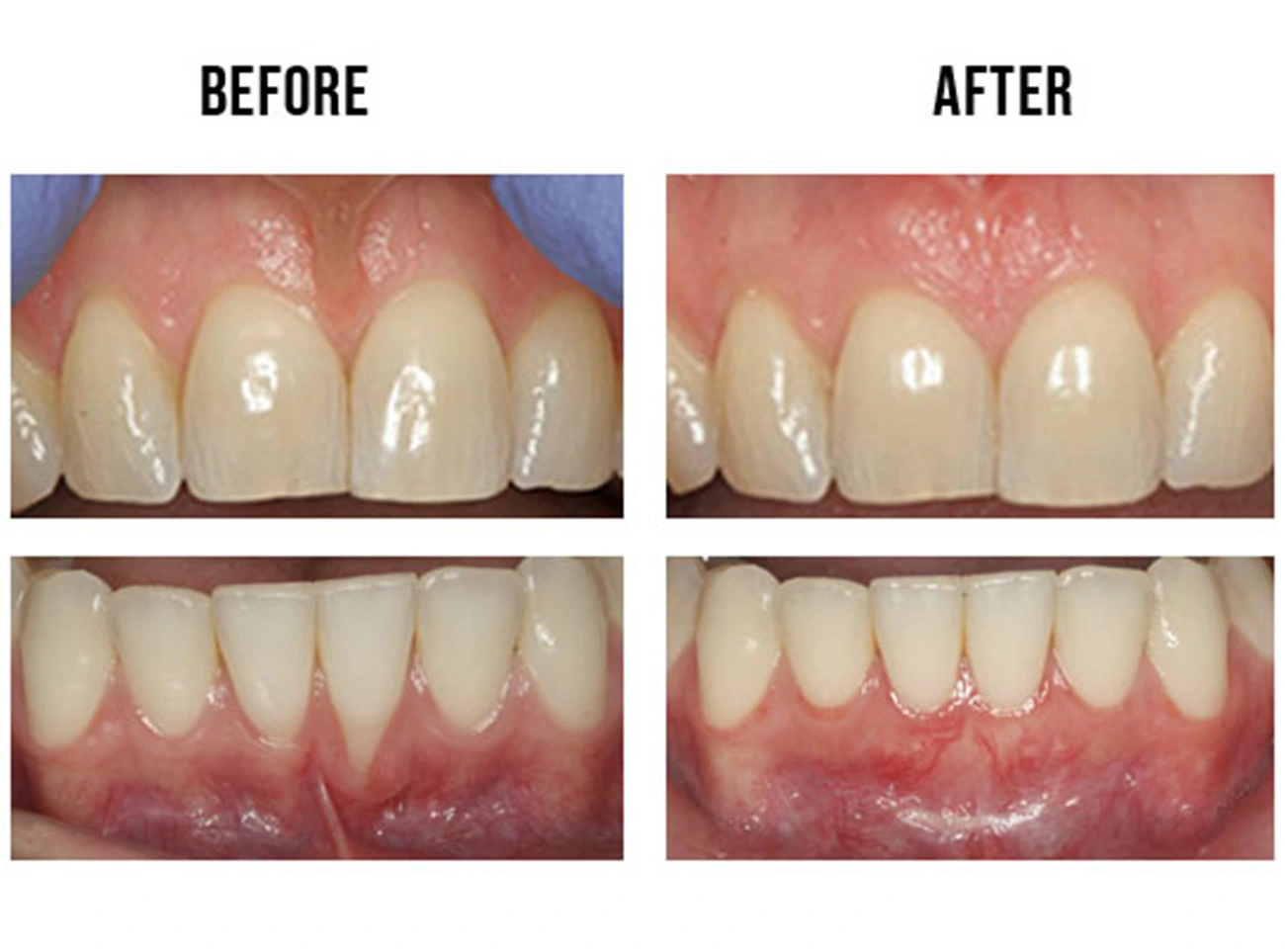
- Labial frenum – A web of connective tissue that links the lips to the gum above the top two front teeth and below the bottom two front teeth.
- Buccal frena – Thin strands of tissue that connect the gums to the insides of the cheeks.
When is a Frenectomy Needed?
An elongated lingual frenum can cause difficulty for infants to nurse or feed from a bottle, and this condition is often referred to as being “tongue-tied.” If left uncorrected until toddler years, affected children may experience difficulty speaking compared to their peers. This condition may not be detected during routine checkups by a pediatrician or dentist and can become noticeable when the child enters pre-kindergarten or elementary school. An elongated frenum may limit the tongue’s extension, and severe cases may result in discomfort while swallowing. Fortunately, a typical frenectomy can be performed quickly and with minimal pain during the first few weeks of birth.
On the other hand, an extended maxillary labial frenum can cause orthodontic problems, particularly if it extends near the gum line. This may interfere with the proper growth and spacing of the upper two front teeth, resulting in a gap between them. Although some parents may worry about the gap’s appearance, orthodontic procedures are generally delayed until the child’s permanent teeth have emerged. If the gap persists after braces have been placed, a labial frenectomy may be considered as a solution to the abnormal spacing. In many cases, the adult teeth’s emergence and growth lead to natural closure of the gap caused by the frenum’s length.
Performing the Procedure
If you or your child are experiencing undesirable side effects of an elongated frenulum, a frenectomy may be suggested as a permanent solution. Your oral surgeon will examine the frenum or frena in question to determine whether the procedure is necessary. Generally, noninvasive approaches are considered first unless the existing frenum is causing difficulties with feeding, such as breastfeeding in infants and toddlers, or speech complications.
The procedure typically takes only 10 to 15 minutes, and recovery is typically complete within two weeks. Pain relief medication may be prescribed to alleviate soreness at the surgical site. Proper aftercare procedures, such as keeping the area clean and avoiding unnecessary movement of the tongue, are explained to the patient before leaving the dental office.
CONTACT US


